
Abstract: A blockchain is a platform controlled only by software rules, often termed a permissionless ledger. As the corporate world has entered into this new territory, it has modified the original vision to create permissioned blockchains. This mechanism, deployed to control anarchic and fraudulent behaviour, both, is familiar and effective, but comes with costs - it shuts out the small business, the engine of growth and innovation.
What would a blockchain for small business look like? From 1st principles, business needs a stable and safe environment, one in which its community is for it not against it. The missing element is the trust that a community can work together to resolve a disaster.
As blockchain isn’t that environment, the big money waits on the sidelines. To build trust onto a blockchain, we add a modicum of classical institutions of governance: a set of rules, and mechanisms to keep people within the rules. But, crucially, we do not need to build a wall around to lock small business out.
We call the result The Governed Blockchain as a 3rd alternative to permissioned versus permissionless ledgers. It preserves the free entry of open blockchains, but imposes rules of behaviour within the blockchain’s Constitution, and methods to feedback responsibility on bad behaviour.
The Governed Blockchain invites the entrepreneur in to build a business with some basic level of safety and security, that their business will not be destroyed by black swans and other disasters. It invites capital to deploy into blockchain to build business, where before, entrepreneurs were holding back.
It should be possible to justify a design for a system from first principles. Our mission is to build the EOS blockchain for everybody [Grigg, 2017a] . [Larimer, 2017] . In pursuit of the mission, we should be asking questions such as:
Who is everybody?
What do they need?
Can we provide it?
This paper lays down the logic for a governed blockchain from one starting assumption of need - trade. It is our hope that from this point, everything else follows.

A governed blockchain is built for business. An example of such a business is the Steem system, a social network or blogging environment built on a custom single purpose blockchain. Another example is Bitshares, a decentralised exchange for trading cryptocurrencies. These two businesses are sisters in model and team, but have completely different missions and customers. The existence of these two, so close but yet so different, and their relative solitude as viable and independent business proposals is significant - it suggests several things:
That, business is possible on the blockchain,
That, there is a wide application space between and around the two use cases, and
That, this application space is currently under-utilised by business.
Why is this? It is our thesis that other blockchains are unsuitable for business. And the very lack that businesses face is that other blockchains are not governed. Let’s build up the case for The Governed Blockchain .
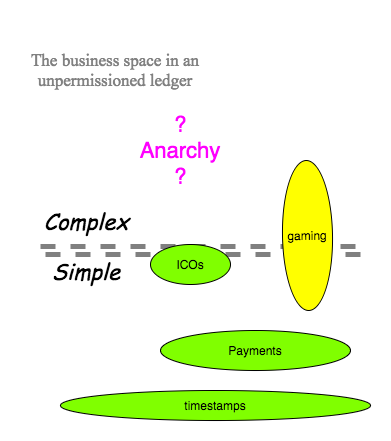
Blockchains have been characterised as unpermissioned and permissioned (Swanson, 2015). This divides the space into (a) open entry, software only blockchains for public access and (b) closed off private blockchains, or ‘walled gardens’ with both software and legal provisions. Let’s consider each in turn.
The original or classical Bitcoin as an Unpermissioned, public blockchain had the disadvantage that with only software-enforced controls, only the things that can be controlled in software will be controlled. Everything else is left uncontrolled.
In effect, this means that there is a relatively stark line between simple and complex: relatively simple things such as payments can be controlled and are controlled because we can code them up. In contrast, complex things such as relying on your counterparty to deliver a swap in a month cannot be so easily controlled.
Hence the seemingly obsessive fixation by the blockchainers on exotic cryptography: multisig, zkSNARKs, ring signatures, Turing-complete smart contracts and other arcania. We must turn the complex into the simple, and without success, unpermissioned blockchains appear exciting but progress so far does not speak clearly or loudly to viable business use cases. The quest continues, even as it has broken many a venture, lost many a fortune and shows little sign of changing that pattern.
Then, complex business with a use case turns to Swanson’s permissioned ledgers in the hope that once so controlled, people will behave and complex trade will start to roll [Swanson, 2015] . Trade begets revenues, revenues begets profits, and profits beget living - all is good. An alternate position to Swanson’s is the consortium blockchain which envisages that the consensus is controlled by a group, but otherwise the chain claims to be open entry, free to trade [Buterin, 2015] .
But permissioned and consortium ledgers face another problem: the person who provides the permissions inevitably owns or controls the chain.
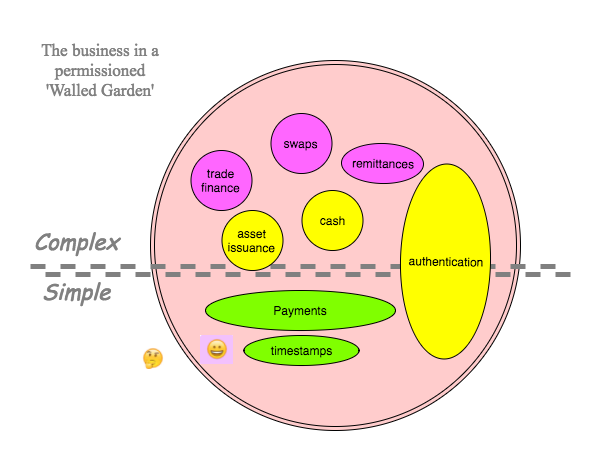
He who permits, extracts. That person that controls the gate seeks to monetise, and adds rules of discrimination to generate pricing opportunities. The owner is also lobbied by other powerful players, and more rules are added to preserve the benefit for the powerful. A further opportunity is that the owner can capture business from users by raising barriers to entry.
Thus the cost rises for all participants, and these chains eventually become dominated by a group of powerful players - cartels following the economic theory if not the political viewpoint. Hence, the term is likely wrong: both permissioned and consortium chains will become private or closed blockchains given enough time and money.
The permissioned blockchain is a closed, private chain.
Free agents see these blockchains as costly. Costs rise, so much so that Internet entrepreneurs do not like permissioned ledgers. The thesis of inevitable cartelisation suggests that the rational entrepreneur knows that the power of the center will inevitably be turned against them, and they conclude it isn’t worth their time and money. The money and effort they invest in the chain has low ROI (“return on investment”), so low it is expected to be negative returns.
Indeed, perhaps, to some, the whole point of the blockchain is that there isn’t an owner, there isn’t a more powerful party, there isn’t a wizard behind the curtain, a central banker behind the coins, a core behind the code. I say, perhaps that is the point, because the design of the blockchain is as it is, the point is as much what we ascribe to it and what we extract from it as any claimed starting position that spawned the first blockchain.
More importantly, what is perhaps becoming clearer is this: everyone can probably agree with the principle that we automate everything that is simple to automate. Whereas, between the two camps either side of the permissioning fence, there is little or no agreement as to what to do with the space of complexity that lies above the line of simplicity.
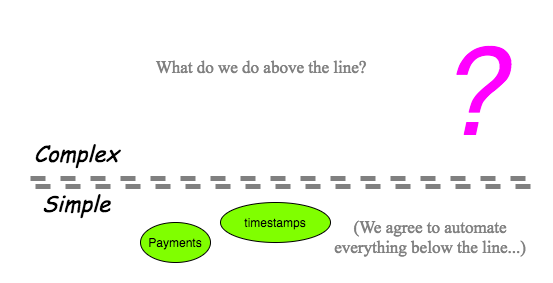
As Charles Evans suggests, we are caught between the Anarchy of the unpermissioned chain and The Leviathan of the permissioned alternative [Evans, 2017] . This is an uncomfortable choice for the small business owner who is asked to invest substantial capital in what amounts to an unreliable future. To analyse our choices, we must go back to the first principles. We must ask what business is trying to do.

If you are a global corporation, finance theory tells us that your best strategy is generally to do what your business already does, until you die. If you are a person with wealth, a high net worth individual, the efficient market hypothesis predicts that your best strategy is to buy the market index, or in today’s lingo, to hodl.
For the rest of us, for the vast majority of humanity, we need to do business to survive. Trade with real goods and services is the beginning and the end of our life strategy.
We put it then as axiomatic that we should build a blockchain not for payments, not for one customer or another, not for banks or bloggers or day traders or gamers or silk roaders or hodlers. Not to please big or small blockers or big or small government.
We should build the blockchain for trade, for business, for all of you.
Business is by its nature complex. As we hinted above, some trade is simple, homogenised, and automated - payments is an exemplary of that in finance. A payment system works at massive scale, is heavily automated and extremely cheap. Such economies at massive scale result in large slow-moving centralised organisations, which also makes them subject to capture and domination by large players. Inevitably: Large banks, large governments, large mining pools.
This is the commoditisation argument - the more simple the trade, the more it is automatable, the more subject to scale, and eventual capture. The takeaway here being that such simple, automatable business is not for us - not for the small players, not for the vast majority, not for the diaspora of small traders. We are competed out, we are excluded. We small traders are squeezed out of simple, scalable trade, but what is left is complex trade. We make our livelihood in that messy chaos where our minds & bodies are our capital, and nobody can squeeze us out of our own minds.
We should therefore build the blockchain for the complex trade.

But with complexity comes errors. We make our money on making the complex happen reliably but errors are the continual reminder: that, fundamentally, what we do is both complex and complicated. If there were no errors, life would be simple. Everything would be automated, the geeks would have won, and we’d be all out of a job! If our customer perceives no risk of errors, they would not pay us a premium for reliability.
It is small trader’s lot to live complex, error-filled lives. We and our errors are yin and yang. Perversely, we have more potential to make more money if our trade is rich with risk. Competition forces us to reduce our rate of error, but profitability incentivises us to keep a healthy ratio of complexity in our trade. As our business becomes more reliable, we compete on a different level - either we seek out more of our customers’ risks to resolve, or we seek to lock our customers in by other methods [Porter, 1979] .
As errors are, they are mostly predictable in class, but unpredictable in the event. Some of our known blockchain risks are, briefly:
That’s for the business of blockchain, and ordinary business is no stranger to risk on or off the chain - there are so many threats and attacks that once listed out, it feels as though no business should survive.
But we do. How do we survive? To keep our errors under control, businesses do risk analysis, which informs us on how to accept some risks, mitigate others, and change our very business to deal with yet others.
There are more clever ways to deal with the future than voodoo - risk management using probability, diversification, mitigation, actuarial science and all that good stuff. Others can get deep into risk analysis, here I shall just claim that while our regular small business person cannot predict the future, she can learn to live with the everyday stress another day in business brings: the tiny chance that today, the unexpected becomes harsh fact. She intuitively prices higher for greater risk, and lower for easy deals. She detects those trades that can break the business, and accepts those that deliver profit worthy of the risk. In short, she trades on the risk of the deal, and she does not risk the business more than any trade merits.
The business owner seems to survive - either she can do risk analysis on her individual trades in her head better than we can write it down on paper, and her mitigations against risks are working, or she’s living her life in a never-ending lottery.
Which tells us what about risk? Let’s look at one of the tools used for formal risk analysis, a risk matrix (Wikipedia “Risk matrix”). [Wikipedia] . This tool measures each risk of error or failure by severity and by probability, and then divides them into three zones - acceptable, as low as reasonably practicable (ALARP), and not acceptable.

In a micro sense the blockchain industry has the right idea - to attack the errors, to reduce the risks. If we can remove or reduce some or all of the errors then surely everyone is better off? But in some high level or strategic sense, the blockchain geeks are missing the big picture of the risks in several fundamental ways:
The upper left hand side is known as black swan risk - incredibly unlikely in the small, but if we wait long enough it’s guaranteed to happen. And when it does, such as happened to the financial system in 2008, we're doomed. In finance they call it turkey risk - the risk that tomorrow is Christmas Day is very low, so turkeys believe Christmas Day never comes.
For responsible business, for users, for our own peace of mind, we need to deal with the unlikely disasters that will wipe us out. We need to deal with our inner black swan.

Where do we find the fabled black swan? In three places: in the backwaters of Western Australia, in the risky writings of Nassim Nicholas Taleb, and on the blockchain:
2011 June 500,000 BTC stolen from Jeb McCaleb’s Mt.Gox auditing account 2013 Bitcoin hard fork from bug in code, rapidly rolled back by core & miners 2013 October 179,342 BTC seized by US agents from ‘SilkRoad’ darknet market 2014 650,000 BTC $323mm stolen from Mt.Gox, handling 80% of BTC trading 2015 April The Collapse of the Bitcoin Foundation 2016 June The DAO - 3.6mm Ether being about $50mm stolen, then fork of Ethereum 2016 August 120,000 = $72mm hacked from Bitfinex exchange 2017 July Bitcoin forked 2017 September China regulates ICOs, orders funds to be reversed 2017 October Ethereum multisig wallets in Parity hit by accidental freeze 2017 November Bitfinex’s Tether dollar unit had $30m reserves stolen 2018 watch this space...
These are just some highlights, but you can see where we are going: disasters on the blockchain are too frequent even to be called black swans.
In the face of the Black Swan, what is the entrepreneur to do? The entrepreneur is very adept at handling small, profitable errors, but the business or market collapsing Black Swan is another matter entirely.
The Entrepreneur invests heavily into his or her business: Programmers, business development, accounting and legal expertise, web development, and a movie's worth of supporting actors. All of these people cost money; an entrepreneur probably needs to find about a million bucks to get the attention of these supporters. You can pick your own number from your own experience, one that could be higher, or lower. But it is going to be a significant and painful number.
Further - opportunity costs are very fierce in the entrepreneurial world. As an entrepreneur, every one of your people faces a choice: to work at a good job at a good firm and earn steady salary, or take on a speculative, low paid, idealistic path to build what could be a fantastic future, but probably won’t be. Only one of five startups make the big time, and that’s after they’ve made it to Venture Capital money.
Whatever number we agree on, the entrepreneur and her team are investing a serious amount of value. The question for blockchain then is,
will the entrepreneur invest their own capital into blockchain?
This question needs to be put against the risks of blockchain. Let’s leave aside the ‘internal’ investor who is already committed to blockchain, can invest in fixing some part of the infrastructure, and can generate internal investment from hodling and ICOs. Let’s consider the external person building a business for users and bringing in external capital. Who, as we’ve suggested above is very adept at recognising risks, and is well able to process the black swan when it swims past.
What does this external, experienced business person think of unacceptable risks? They are too frequent on the blockchain. I suggest to you:
the sane, rational calculating business person does not invest in such uncertainty.
For the business person to come in, rationally, we need to find another way. Business people won’t accept the black swans, just because. Therefore,
We are building the blockchain to solve the black swan.
Fixing a black swan that devastates your new blockchain-based business, but maybe not that of others, is a big ask of the community. For your counterparty and your community to make themselves vulnerable to your misfortunes, on your say so, requires trust. They will need to trust you are telling the truth while they agree and implement emergency changes that put all at risk. For example, the 2013 Bitcoin hard fork incident was handled because once the emergency was spotted, trust allowed the key stakeholders to come to consensus quickly [Narayanan, 2015] .

Controversially, it only took a very few miners to switch their software version back and force the chain back to the earlier fork - contrary to how we expected decentralisation to play out. A similar process launched the 2016 Ethereum DAO repair, but with less success - although the trust in the dominant stakeholders was enough to make a decision, it wasn't enough to follow through to implementation. Not all of the community put full trust in the decision, and fought the patch to war cries of “code is law.” The Ethereum forked into two, becoming Etherea.
Before we ask how the goal should be met we need to be comfortable with the existence of the goal - to solve for the black swan. The challenge for new business is to understand whether the environment supports the resolution of these serious errors: is your counterparty willing to work quickly and fairly to resolve errors? Is your blockchain resilient to external hacks, both before and after? Will a miner return a fat finger error that would otherwise send you broke? Which event has happened in Bitcoin.
Can you repair a broken smart contract? As of the time of writing, the Etherea do not know the answer to that, and worse, they do not know what happens to a real contract after forking [Grigg, 2017b] .
These are billion dollar questions - but they are also hundred dollar questions. Although we came to the question via the utter disaster known as the black swan, for a business, the question is broader: Can you fix problems? How? And how costly? Which latter admits that there is no guaranteed fix, but this we already know - business conducts analysis of its risks.
And, this question ultimately reduces to another question: are you with me or against me?
Huch nobHa'bogh verenganpu''e' yIvoqQo'
Don't trust Ferengi who give back money
Klingon proverb
The incidents above, both successful and debacled, suggest that fixing problems is possible, even if controversial. Business wants us to be able to handle several classes of failure, and in principle, we want detailed answers to a greater or lesser degree for the failures listed above (II. "Error, be gone!").
The choice is stark: Cooperate or Fight.
We can cooperate to solve problems, if we have trust, as did the core devs in 2013.
Or, if we expect insufficient trust on the part of the others, we can fight, as we found with the Mt.Gox, the DAO, the "classics", and a thousand other hacks. Without the expectation of cooperation, in an environment of untrust, your capital can be stolen or destroyed by those who are smarter or more adept than you.
Worse, if you can't beat ‘em, you join them: you play it fast, footloose and fancy free, and steal or destroy the capital of others. Either way, the blockchain of adversaries may live on but your own financial future is likely nasty, brutish and short.
There are other ways to look at this divide. Here’s several taken from varied disciplines.
Negotiation Theory The master negotiator seeks a good trade for both parties in a process called win-win. This goal of sharing the win with your other party assumes that there will be follow on trades in some sense - you want your other party to be happy to come back, and also to spread your reputation for fairness far and wide. She wants the same.
As well as routine business, this theory suggests that cooperative trade with win-win negotiating should be the basis of family and employment negotiations, simply because both of these guarantee that there are new negotiations coming soon.
The alternate to win-win is called win-lose. For me to win, you must lose, and vice-versa. This negotiation occurs when there is no apparent follow on trade. The problem with this approach is that, for one side to win, the other side has to lose. If you don’t know which it is, then it’s probably you.
Hence this adversarial approach is reserved for shady business. Especially buying houses, used cars and lawsuits in court are the places where the decision is done on the day, and there is little or no benefit in the future to not fighting for every last crumb.
Economics When we can both take something positive from our trade, economists call it production, because something extra has been produced by our combined efforts. For example, if one of us has a kitchen, one can provide some ingredients, another has a recipe, and one can cook, we can come together to bake a cake - or cookies, or pie, you pick. The result is that now we have a pie, and that’s better than before. We have produced, and now we can share the fruits of that production.
The alternate is called allocation: when someone (else?) has cooked a pie, and we only get to decide who gets which portion. This pie is made, there is no sensible play where we can make a larger pie out of a smaller one. Assuming that we don't walk out with the same sized slice of pie, then one of us is likely to win a bigger slice, and the other must walk out with a smaller slice!
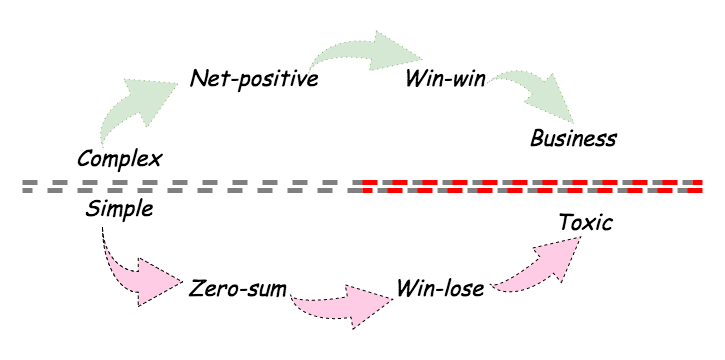
Game Theory If a game results in growth it is called a net-positive game. The players come out with a better situation than that which they entered. The alternate to the net-positive is called the zero-sum game in which the value at the beginning is the same as at the end. Who benefitted and who lost? Political Theory Capitalism [Gupta, 2014]: Nationally enforced rule of law creates skin in the game for everyone that goes beyond the current trade. Dishonest statements or lack of integrity can be brought to complaint, but all are vulnerable to the system.
Anarchy: Voluntary rules of interaction leaves no skin in the game beyond the present stake, thus allowing the sharp trader to out-compete the dumb trader. All are vulnerable to caveat emptor.
For the entrepreneur, all of these views end up on the same side of the fence - she wants to be on the left side so she can get some certainty about the safety of her investment. In particular, she wants to have her damages looked at in the event of disaster, even if the nominal result of “you lost” is all she gets back.
For Alice the trader to know that Bob the entrepreneur is on her side of the fence when disaster strikes is a question of trust. Building a productive business in complex space, over the long term raises the fear of her capital being raided - can she trust her community to be there when she needs them to help?
Trust then is a desirable property. But where does she find it? Is Trust a place, a service or a religion? Can the entrepreneur buy it at the supermarket like I buy beer?
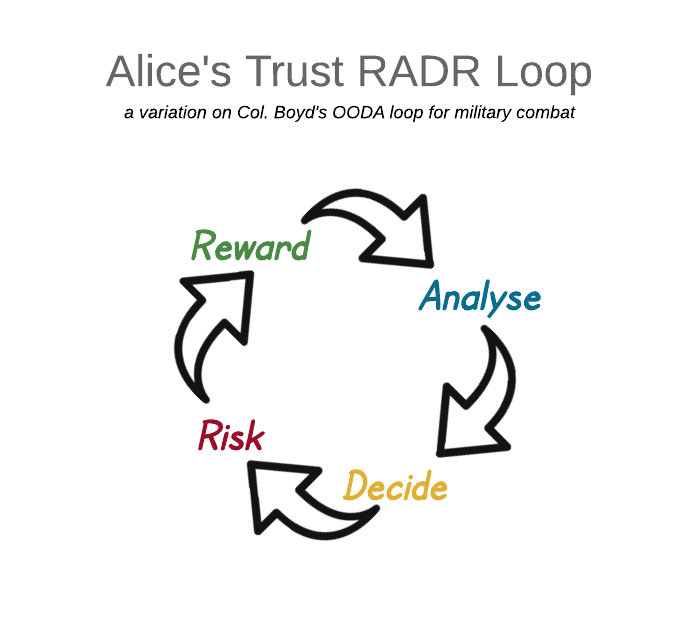
Thinking about when you and I find trust with each other helps to set a framework [Grigg, 2016] . Game theory tells us that to build up the big trust, we need:
I won’t trust you much after one beer, one meeting, one argument; I am much more likely to trust you after 100 beers, 100 meetings, 100 debates, by which time we’ll both know I’m untrustworthy about counting the beers.
Each of those 100 events requires a decision, and each adds some information for the next decision. This risk analysis is a cycle: analyse, decide, take on the risk, and enjoy the reward (or not!). We both need to remember the outcomes for the next time, and tag that information with the identity of our partner.
Then, trust comes at a high cost, and by its nature, it is too expensive for one trade.

If you require trust with me as your counterparty, the only way to make this workable is if we establish a framework of repeated trades. That is, we spread the cost of trust that fixes the one big snafu over many good trades that each have a little margin devoted to building trust. The building of trust into relationship is made of many small bricks: Introductions, information exchanges, trial transactions, user support, minor teething problems, finding those lost transactions. We hope that enough trust is built in time to capture and tame the black swan when it flies in.
Spot the flaw: trust is expensive. We need to 'amortise' or share the cost of all of these small steps. And for that, we need to rely on repeated business, and the expectation of repeated business.
Perversely, trust requires repeated trade and repeated trade requires trust - you are not going to engage in the process of building trust over multiple rounds unless you trust me to at least buy the next round.
Which is to say, right now, we may be cooperating on today's trade, but we are expecting every future trade we might also be involved in. We therefore require a blockchain that is cooperative, for all trades, all persons and all tomorrows, rather than adversarial, for the one big win today.
Blockchains have been lauded for their history, their immutable past, their lock on that which has happened, indeed their trustlessness. But this is to look backwards, to history, to archeology, to dead data. People who trade look forward because all trust builds towards a better future.
We build the blockchain of the future, in which all our tomorrows are anticipated, in which the long term is the term.
Without the future, trust cannot be.
“[Global Thermonuclear War is] A strange game.
The only winning move is not to play.
How about a nice game of chess?”
Wargames 1983
We can see something of the answer in the divide between humans and machines. Only humans can engage in net-positive trade, because only humans can value the results. Machines are incapable of production because they cannot value; the best they can do is automate the allocation of value that already exists, and assist in production for their owners.
Value belongs to humans: Pie and cookies are enjoyed only by humans. The appreciation of the results can only be enjoyed by the humans, because humans alone can make the subjective and emotional decision as to what is to be enjoyed. We can employ and own machines to assist in production, in the creation of positive value, but production can only occur because we value it so, because we ascribe a positive value to the results as against the inputs.
Machines then are limited to an allocative approach, win-lose, to fight, to extract, to play until death, whereas us humans have choice - we may play at win-lose, or we may also cooperate, or even switch our strategies because we don’t feel good about the other person. We may not play at all.
Yuval Noah Harari says that what makes humans special is our ability to create fictions or beliefs around which we can choose to cooperate at scale [Harari, 2015] . But none of this works if there is no choice, no risk, and damningly, no reward that can be enjoyed. We can build an AI or robot to engage in (say) high-frequency trading, splice a gene, or predict dating partners. But we cannot build an AI to enjoy early retirement off of a lifetime in the markets, to sip a margarita in bliss, to watch a sunset with a partner or share joy in bringing up a child.
Machines are therefore locked into an allocative game, and absent sophisticated and brittle AI techniques, they find themselves best able to engage in win-lose, in the zero-sum game. Two machines playing any game or protocol can only move existing value back and forth, they cannot create value.
This is reflected in the relative strength of the blockchain as an allocative method, below the line, and the relative weakness that the users and their smart contracts have found themselves in, above the line. In principle, this is sane and rational - before, we said that we should automate the simple, as much of the simple as we can. That which is complex, we leave above the line, for the humans. Therefore, correctly, blockchain places the choice above the line with humanity - win-win or win-lose, your choice, your smart contract, your enjoyment.
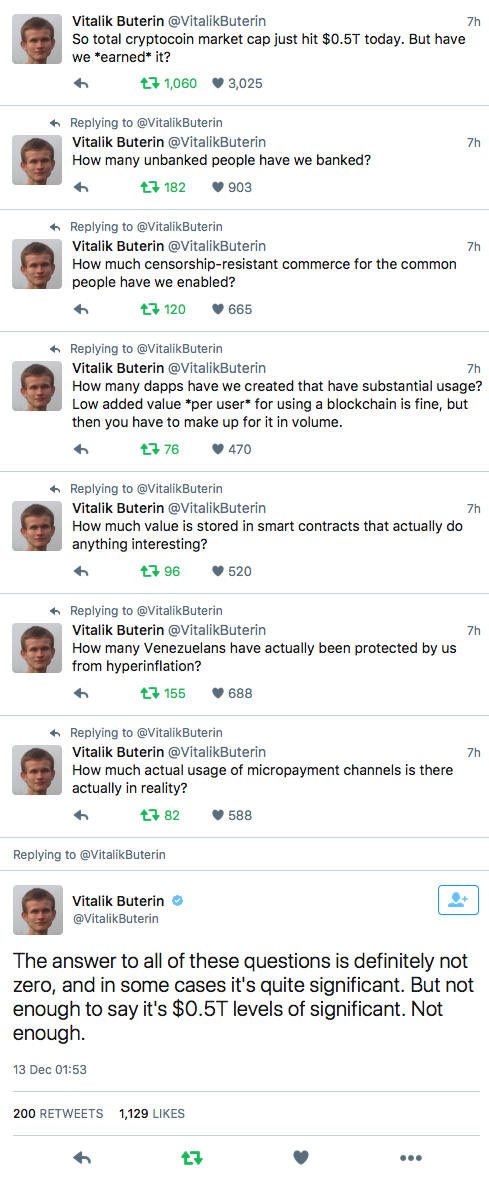
“How much value is stored in smart contracts that actually do anything interesting?”
Vitalik Buterin, tweet 13 Dec 2017
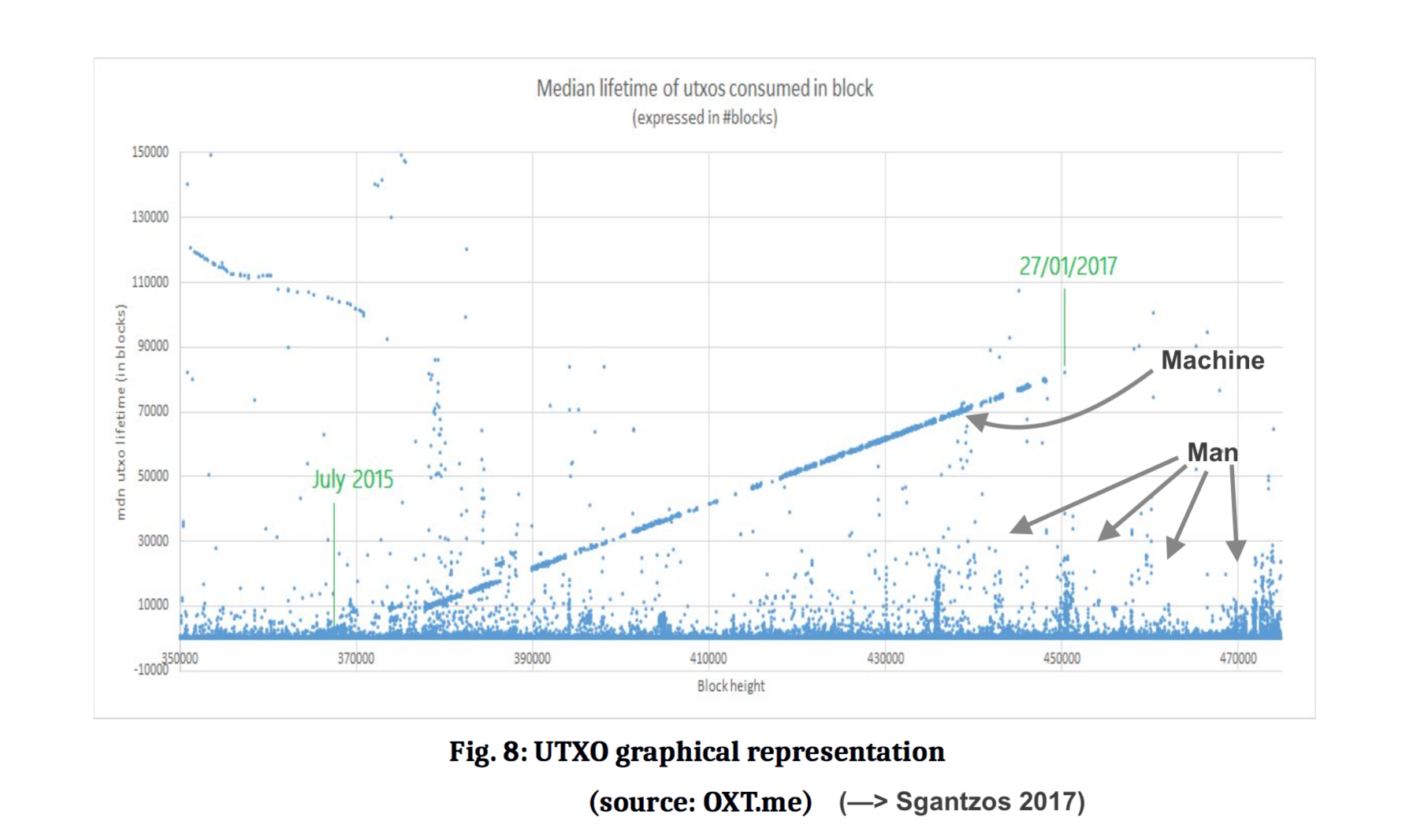
The unpermissioned blockchain spends most or all of its strength below the line. Whether that user proposition be a payment or a series of simple “script” instructions, a virtual machine or a genetic algorithm trained to respond to questions of import [Sgantzos 2017], it is still automated, and it is left to the user to turn that base tool into valuable trade.
Satoshi’s design is justifiably seen as a breakthrough. The blockchain can complete simple trades automatically, at the allocative level of the zero-sum game; it defers complex trades of a more win-win, productive form to the complex layer, what might also be called smart contract space. The complexity of trade, as epitomised by the technical promise of smart contracts, is exciting to many.
Yet, it is somewhat clear that this latter part did not emerge, or was excruciatingly slow to do so. Why is this?
It may be that Satoshi's design so successfully solved the automation of payment and other simple tasks that the community put the win-lose on a taller pedestal than otherwise deserved. The solution was good at bringing together otherwise adversarial parties to trade, but there is no necessary conclusion that, just because the blockchain can solve an adversarial allocative trade in simple space, that complex space should likewise be adversarial, allocative, win-lose or zero-sum, either individually or in combination.
Above, indeed we present the entrepreneur as one potential user who does not want that. And has walked away in frustration. It is not just the absence of attention to this need, nor the weakness of tooling & solutions, nor the blasé attitude to end-user security. Rather, blockchain today has gone far further in its idolatry - the community champions the adversarial, the allocative, win-lose, zero-sum as the space in which to trade. It is as if the blockchainers say, “we've discovered trustlessness is the answer, and now trust is banned!”
And this is the trap that the UnPermissioned blockchain community has fallen into - the outcome of championing an allocative game is the promotion of an incompatible environment for constructive trade.
The obsession with the allocative approach has consequences. While a trader is concentrating on today’s big win, she is not concentrating on production. If she does win big, then her customer will lose big - and may not be there tomorrow. If on the other hand she loses big, she may depart the scene, with a bitter taste, big losses and no good word to say about blockchain.
Multiply the individual poverty across the community, into debates, chatrooms, decisions, divorces and other bankruptcies - the obsession presents a high barrier. It will over time act as a filter: those people who want to produce, have the patience to build, those who see the value in the long term, the trust will be excluded. Either by frightening them away, by chasing them away, or by win-losing away their value.
While, the easy winners are rewarded and encouraged to stay for another easy kill. If the environment promotes zero-sum trading then zero-sum traders are what will make up the community. If we can label that as a community.
In Satoshi's view, technology can effectively route around the human "design flaw" in the present money system. Satoshi’s Bitcoin, therefore, is built to be incorruptible by human operators. Bitcoin champions a form of techno-absolutism that insists on properly designed technology as the solution to any social problem. This spirit of techno-absolutism attracts like-minded people who are fascinated by the mistaken notion that technology can fully "replace" politics or human decision making. Conjoin Bitcoin's techno-absolutism with an anarchic rejection of institutional authority and a libertarian commitment to property and privacy, and an unique social ideology emerges. It’s an ideology that is espoused by Bitcoin’s technology (i.e., its technology thesis) and it also permeates the community.
[Panchèvre, 2015 (my emphasis)]
It gets worse. The win-lose approach to trade (think: real estate, used car selling and financial products) has now moved to center stage. This brings in people talented at the hard sell, the one off, the deceptive offering, the kill.
But, as the wrong type of trader permeates a community that also champions anonymity and an absence of standards or ethics, the line between aggressive trading and crime dissolves. Anything goes; it becomes rational to do what you can - as long as you don't get caught.
By way of rhetorical examples:

If you look around the blockchain space and can't tell who's getting scammed, it's probably you.
Jameson Lopp, tweet 23rd September 2016
The earliest report of a possible crime is Jeff Garzik's report of an overflow bug being exploited in August of 2010 - some 184 billion were minted through abusing the limit of an integer at 2^64 size [Garzik, 2010] . Many followed. Indeed, many of the above list of black swans were criminally motivated. Which takes us from the early innocent days to the present brutal reality:
Unpermissioned Blockchain is not only win-lose, it is encouraging of crime.Attracting the sorts of people who can work effectively with win-lose and scaring away the rest is a self-fulfilling destiny in toxicity - BTFD, FOMO, and YOLO are rallying cries, anything goes becomes the climate, and crime follows close behind [Güring&Grigg, 2011]. We start with those who understand the haggle, the trade, the pop, the win in the short term. And we invite those who relish the easy money, the pump & dump, taking money from new players, the big kill. Followed by the crims.
In the final outcome, the unpermissioned blockchain fails to support business. Not because unpermissioning is a bad idea, but because an environment of zero-sum games promotes zero-sum behaviour, and squeezes out net-positive opportunities of productive trade. In a word, unpermissioned blockchain is toxic.
If your goal is money, you'll develop a destructive personality, as the world appears zero-sum, your desire is for others to do things for you. If your goal is liberty, you'll develop a constructive personality, since your world is your own creation.
Mark Wilcox, tweet 13 April 2018
We can test the win-lose hypothesis: today's blockchains are where we automate payments, gaming, ICOs and exchange of crypto. The popular successful applications on Bitcoin and Ethereum are almost exclusively zero-sum games:
"if you look at State of the Dapps, the large majority of working applications are either for betting, gaming, or facilitating the movement of ether."This is the world of day traders, banks, pumpers & dumpers, private dealing, financial engineers, cartels and so forth: the house always wins, cartels are held together by self-interest, currencies such as BTC can only allocate and any 'gains' are because new buyers cash out the old buyers. There is consensus in transactions, but as we know from game theory, any faith you derive from these transactions is not long-lasting.
BlockMason, tweet 2017

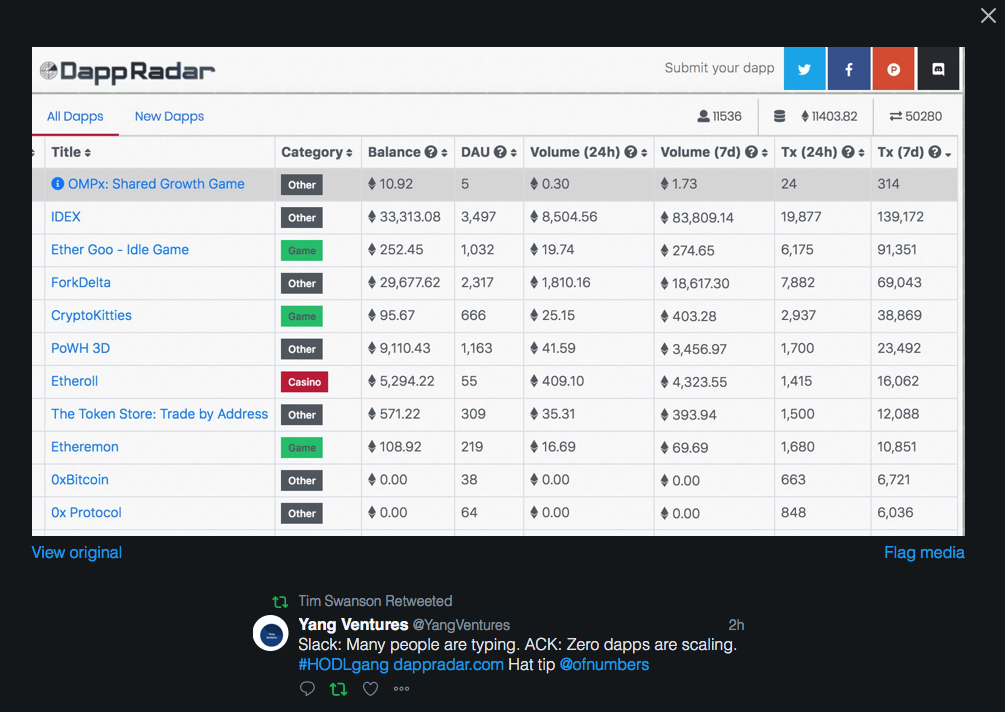
What are the net-positive businesses? To our knowledge, there are only two distributed applications in the entirety of crypto space that are productive rather than allocative:
If anything, CryptoKitties as a productive application highlights how far we haven't come - we've created a $500 billion industry in which the major crimes outnumber the major productive businesses.
Who shut down BTC-e?
It wasn't the enterprising efforts of the cryptocurrency community or its verbose opinion-makers on social media or the "new 1%." It was several government law enforcement agencies that coordinated across multiple jurisdictions on limited budgets.6 Yet, like Silk Road, some people in the cryptocurrency community likely knew the operators of the BTC-e and willingly turned a blind eye to serious misconduct which, for so long as it continues, represents a black mark to the entire industry.
[Swanson, 2017]
If the opportunity of unpermissioned blockchain in blockchain is winning or losing, then the outcome is destruction or denial. It’s hard for the small enterprise to make profits in a toxic environment. Encouraging the talents of war and appropriation has the effect of discouraging the talents of peace and trade. Which is fine, if we’re actually fighting a war, but what if we’re not? Such an environment does not welcome those who have the patience to build a business, those who see the value in trust.
Unpermissioned blockchains promote the zero-sum game therefore discourage business with aggressive win-lose, when business is by its nature built on the alternate, win-win. This is the fundamental reason why there have been few stable businesses in blockchain outside the zero-sum game - no rational business person will invest their capital in a toxic environment full of arguments & insults, thefts & hacks, risks of forks and the like.
In small business, we look for the trade that is a positive sum, because we want our customer to come back. We both win a little each time, and therefore, a win-win overall. We cannot grow as a society unless we all make profits together.
Therefore we must, in order to serve people and business, construct a blockchain that is encouraging to win-win, to net-positive trades. And while not discouraging of the allocative trade, which granted is an essential part of trade because of its simplicity, we do want to discourage the win-lose trader from taking center stage and thereby displacing the win-win trader.
We want to attract and incentivise the right sort of people, these that want to do good trade and make shareable profit; we want to discourage and filter out the wrong sort people, those that want to take the crumbs off the table, those that beggar their neighbour, and those that steal.
A blockchain for business is one that promotes win-win, productive trades over win-lose, allocative trades.
It is to that more refined goal we turn in the next section.
Our challenge then is to move the blockchain agenda from supporting the win-lose at the expense of the win-win, to supporting the win-win over the win-lose.
This is not to say that the zero-sum game, or that win-lose should somehow be forbidden. It's rather to say that our focus is on the win-win because that is where society creates value. Society loses money on the win-lose trade, which is why banks and bankers get richer and people get poorer and those countries that bailed out the banks in 2008 at the expense of the economy are in secular depression. Society - all of us - only create value when we work together and each take a profit out of the trade.
To encourage win-win we need to provide:
That latter is a new thing. Skin in the game says that we need a method for Alice to hold Bob to account when he acts up. The method needs teeth, so that the value in play is at risk. We need a structure where our community members can guard themselves against an aggressive party turning a trusting win-win trade into a win-lose by trick, just bad trust or downright crime. There must be repercussions for such actions, there must be skin in the game, so as to hold that aggressor to account.
A permissioned ledger provides for this, yet the process described above defeats it for the small player.
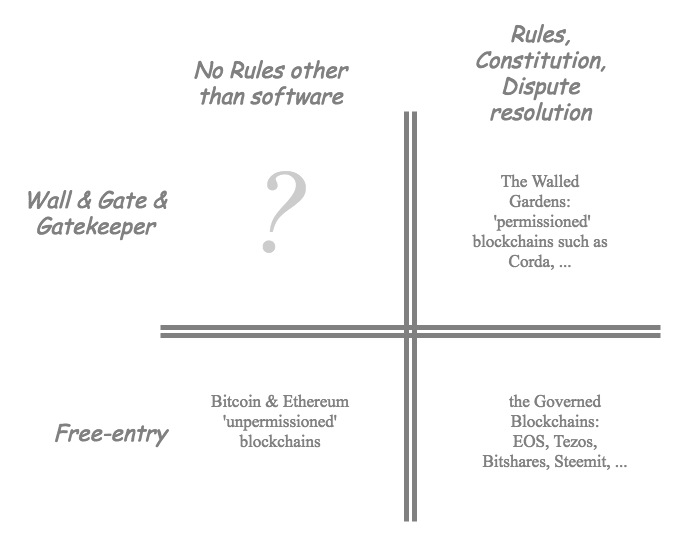
Why is that? A permissioned ledger consists of, let’s say:
The problem - the difference between the two above descriptions - is the wall. Let's put them side by side:
- ◯ A wall around the garden
- ◓ A gate and a gatekeeper
- ⇒ Open entry & exit
- ⇒ repeat transactions
- ☆ A set of rules,
- ☆ A method for applying the rules
- ☆ Consequences
- → Rules of the game
- → a way to trade
- → Skin in the game
Once there is a wall, we have to have a gate to get into the garden. And once we have a gate, we have to have a gatekeeper. We outlined the barrier to entry costs of the gatekeeper above, but there is another cost we did not mention: Regulation.
Unless someone invents a decentralised wall (!), a decentralised gatekeeper (!!) and a decentralised gate (!!!) then the gatekeeper will be subject to both internal pressures and external pressures. To cut a long story short, our gatekeeper will come under some regulator's control, and will then proceed to place all of the regulator's choice rules in place.
See the problem? Pretty soon we'll be back to centralisation, to being a bank and needing a banking licence. Then everything will clog up and we'll be praying for another 2008 style bailout and a decade of stealth bailout, also known as Quantitative Easing.
A decentralised community cannot be beholden to a gatekeeper. If you're unsure of this, talk to the compliance department of any fiat exchange. Free entry has to be preserved in order for the result to be a community blockchain. Therefore, the decentralised community cannot have a wall nor a gate nor a gatekeeper.
Let's tear down the wall.
As well as being aligned to the concept of win-win, the rest of the elements above ☆ are not so forceful as centralising influences. In other words, they are not so controllable from outside the environment of your community’s blockchain. It turns out that we can decentralise these elements and create our system of governance with control in the hands of the community.
In brief, opening the Walled Garden into perhaps an Open Park with a posted notice board looks like this:
Why does this work? Firstly, the will of the community. It is not the wall that holds the person to account, it is the community, using the tools found inside. The rules are enforced by the members according to a process that is already agreed.
Secondly, in economics terms, the constitution forms a Schelling point to which everyone agrees on entry. This agreement, this constitution is sticky - when push comes to shove, most will stick to the rules, because they see that most will stick to the rules.
Then, the grievances can follow a path agreed by the community. The rules direct their grievances to the Arbitrator, who creates a Ruling, which can then act as a call to action encouraging the community to enforce. As the system starts to work, supporters gather and the process becomes the Community.
Finally, signalling: those smart criminals who are looking for easy marks will realise there are barriers here that will cost more and raise their risks. The the rules and rulings act as a filtering device. Crooks then analyse whether it is better to go to some other garden.
There are three missing elements in this description which we have to leave out of scope.
One is Identity. As a consequence of the need to build trust over an extended series of trades (Alice’s Trust RADR above), Alice needs to be able to remember Bob and recall how her last decision went, before she relies on him again. Identity is a very deep and interesting topic in itself, but it is too big for this essay; interested readers are referred to the Identity Cycle [Grigg, 2015-2018] .
Second, the technical security model. Multisig arrangements, recovery partners, time-delay transactions, staking and hardware wallets are all useful components (Larimer, 2017) that when deployed in concert with a strong Constitution and Arbitration framework will make the job of the criminal much harder.
Thirdly, how to impose the Constitution on entry? This can be handled with a mix of two elements. (1) Technically by making the Constitution into a Ricardian Contract - one which is both machine and human readable, and critically has its hash placed into any relevant communications with users [Grigg, 2004]. Then, (2) legally, by having the Constitution include a clause that describes how third party operators and developers take on the responsibility for fairly presenting the Constitution to users. Their software can then ensure that users enter into the agreement, as signalled by the presence of the hash, to which all recipients may rely. Interested readers are referred to NortonRoseFulbright's "Legal Analysis of the Governed Blockchain" [NortonRoseFulbright, 2018].
"The principle of open entry is important for blockchain robustness, yet open entry can also occur within a range of actors that does not include the whole humanity, but only those that accept some rules and satisfy some requirements."
[Morini, 2017] .
A governed blockchain is one which has free entry, but conditions apply on entry (Morini 2017). Primarily those conditions are rules of behaviour, encoded in a Constitution, and include two critical elements: a forum for dispute resolution and a method for changing the rules.
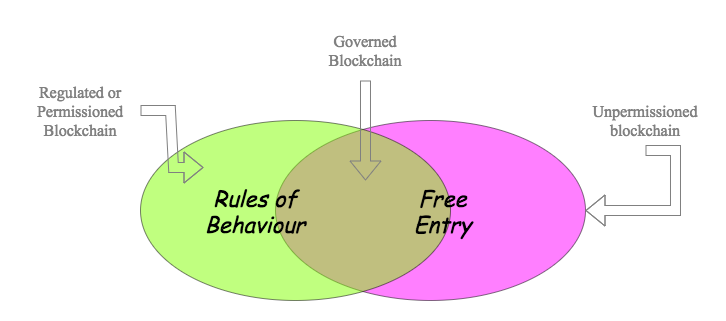
We present it as a third alternative to the permissioned and unpermissioned blockchains (Swanson, 2015).
Up until recently, blockchains had been characterised as unpermissioned or permissioned, and this was thought to be the only choice. More limiting, to a large extent it was believed the two are incompatible, the choice is exclusive.
We offer a third choice, the Governed Blockchain. By identifying the components that differ, we find that one component - free entry versus the wall - is key, and it can be modified to create a third, safer alternative suitable for business.
A community of enforceable rules creates an open garden. A community in an open garden can cultivate win-win trade for the people. A community of win-win traders can build an economy for their mutually beneficial future. And finally, a mutually protective community can finally invite in the mass market.
[working draft] "The Governed Blockchain" - google docs https://docs.google.com/document/d/1TKegYdH5ASqGlEWiVDYFMubE7651hsZIuZb8FKO8KNk/edit#.
[Grigg, 2017a] Ian Grigg, 2017a; "EOS: An Introduction," iang.org/papers/EOS_An_Introduction.pdf
[Larimer, 2017] Dan Larimer, 2017; "EOS Technical White Paper," github.com/EOSIO/Documentation
[Swanson, 2015] Tim Swanson, 2015; "Consensus-as-a-Service," http://www.ofnumbers.com/wp-content/uploads/2015/04/Permissioned-distributed-ledgers.pdf
[Buterin, 2015] Vitalik Buterin, 2015; "On Public and Private Blockchains," https://blog.ethereum.org/2015/08/07/on-public-and-private-blockchains/
[Evans, 2017] Charles Evans, 2017 "Delegated Proof of Stake: Between Anarchy and Leviathan," working paper forthcoming.
[Porter, 1979] Michael E. Porter, 1979; "How Competitive Forces Shape Strategy," Harvard Business Review Vol 59, No 2.
[Wikipedia] Wikipedia, "Risk Matrix," wikipedia.org/wiki/Risk_matrix
[Kerckhoffs, 1883] Auguste Kerckhoffs; "La cryptographie militaire ('Military cryptography')," Journal des sciences militaires, vol. IX, pp. 5-38, Jan. 1883, pp. 161-191, Feb. 1883. http://www.petitcolas.net/kerckhoffs/la_cryptographie_militaire_i.htm Kerckhoffs' 6th Principle is, "Finally, it is necessary, given the circumstances that command its application, that the system be easy to use, requiring neither mental strain nor the knowledge of a long series of rules to observe."
[Narayanan, 2015] Arvind Narayanan, 2015; "Analyzing the 2013 Bitcoin fork: centralized decision-making saved the day," Freedom to Tinker blog https://freedom-to-tinker.com/2015/07/28/analyzing-the-2013-bitcoin-fork-centralized-decision-making-saved-the-day/
[Grigg, 2017b] Ian Grigg, 2017b; “Life is a Cabaret… Or how to split and merge a blockchain,” Financial Cryptography steemit.com/eos/@iang/life-is-a-cabaret-or-how-to-split-and-merge-a-blockchain
[Gupta, 2014] Vinary Gupta, 2014; "[Bitcoin] Cannot be divorced from pre-existing political theory," IAmSatoshi Interview, youtube.com/watch?v=FHFSvttMg6E
[Grigg, 2016] Ian Grigg, 2016; "On Trust," working paper, Part II of Identity Cycle.
[Harari, 2015] Yuval Noah Harari, 2015; “What explains the rise of humans?” TEDGlobalLondon https://www.ted.com/talks/yuval_noah_harari_what_explains_the_rise_of_humans
[Sgantzos 2017] Konstantinos Sgantzos "Implementing A Church-Turing-Deutsch Principle Machine on a Blockchain," forthcoming, HSCBB 2017
[Panchèvre, 2015 (my emphasis)] Ian Maya Panchèvre, 2015; "Immaterial World:The Virtual Politics of Bitcoin."
[Garzik, 2010] Jeff Garzik, 2010; "Strange block 74638," Bitcointalk
[Güring&Grigg, 2011] Phillip Güring & Ian Grigg, 2011; "Bitcoin & Gresham’s Law - the economic inevitability of Collapse," working paper
[Swanson, 2017] Tim Swanson, 2017; "Eight Things Cryptocurrency Enthusiasts Probably Won't Tell You," working paper
[Nagy&Shakel, 2008] Daniel Nagy, Nadzeya Shakel, 2008; "OpenPGP-based Financial Instruments and Dispute Arbitration,” Financial Cryptography 2008,
[Grigg, 2015-2018] Ian Grigg, 2015-2018; Identity Cycle, working cycle of papers, at https://drive.google.com/drive/u/0/folders/0B9aJ9_ZDMOjMbVRIMUNZdUJLakU
[Grigg, 2004] Ian Grigg, 2004, "The Ricardian Contract," First IEEE International Workshop on Electronic Contracting, iang.org/papers/ricardian_contract.html
[NortonRoseFulbright, 2018] Adam Sanitt & Ian Grigg, 2018; "Legal Analysis of the Governed Blockchain," NortonRoseFulbright, forthcoming
[Morini, 2017] Massimo Morini, 2017; "2018: The Year We Make Cont(r)act," Coindesk